Accessibility isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental necessity. And as technology continues to shape our lives in profound ways, making sure everyone — regardless of ability — can access and interact with digital content is not only the right thing to do, but also a smart business decision.
The International Design Foundation describes accessibility as “the concept of whether a product or service can be used by everyone — however they encounter it.” Since accessibility is often confused with usability, this group created a graphic that is helpful in understanding the differences.
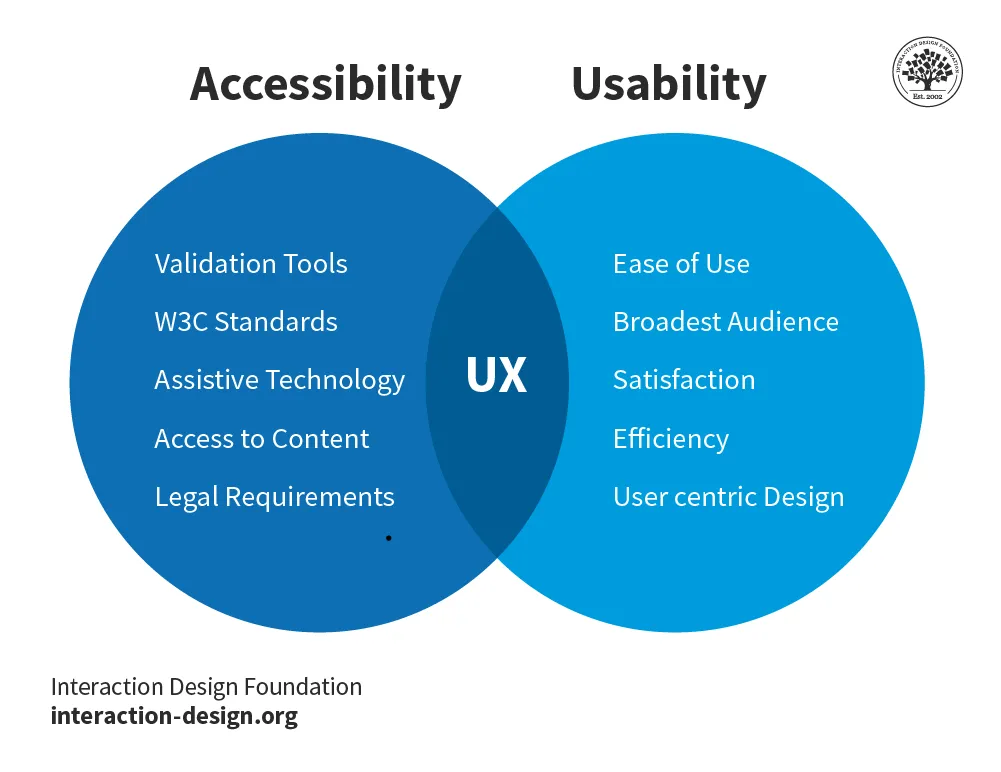
Accessibility refers to designing software that is user-friendly and inclusive, ensuring people with disabilities can also fully engage with the software’s features and functionalities. By prioritizing accessibility, businesses comply with legal requirements and also tap into a broader customer base, while improving user experience for all.
From a branding perspective, incorporating accessibility into custom software development can help organizations build a reputation for inclusivity and empathy. It shows how a brand values all its users, regardless of their abilities. And it demonstrates a commitment to providing equal access to its products or services.
Accessibility in software development has a significant impact on search engine optimization (SEO) and organic rankings. By making software accessible, it becomes more easily discoverable by search engines, leading to increased visibility and organic traffic.
Building software from the ground up for everyone
When it comes to software, “accessible” means considering the needs of all individuals with disabilities, such as those with visual impairments, hearing impairments, motor disabilities, cognitive disabilities or ability barriers. This includes:
- Providing alternative text for images
- Captioning videos
- Using color contrasts that are readable for individuals with color blindness
- Providing keyboard navigation options
- Ensuring the software is compatible with assistive technologies
Implementing accessibility features from the beginning of the software development process is essential. It is much more difficult and costly to retrofit accessibility into existing software than to incorporate it from the start. By considering accessibility as an integral part of the development process, businesses can proactively create software that is accessible to all users.
Understanding accessibility standards and guidelines
To ensure software is accessible, designers and developers need to understand and adhere to accessibility standards and guidelines. These guidelines provide a framework for creating inclusive software and cover various aspects such as web content accessibility, mobile app accessibility and software interface accessibility.
One of the most well-known accessibility standards is the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The WCAG provides a set of guidelines and success criteria for making web content more accessible. It covers areas such as:
- Perceivable content
- Operable interfaces
- Understandable information
- Robust technology
In addition to the WCAG, there are also specific guidelines for mobile app accessibility, such as the Mobile Accessibility Guidelines developed by the Mobile Accessibility Working Group (MAWG). These guidelines address the unique challenges and considerations of creating accessible mobile applications.
Common accessibility barriers and how to overcome them
While accessibility standards and guidelines provide a roadmap for developers and designers, there are still common barriers that need to be overcome to ensure true accessibility in custom software development.
Lack of awareness or understanding of accessibility requirements among designers and developers can be a barrier. Many designers and developers may not be familiar with the specific needs of individuals with disabilities or may not know how to implement accessibility features effectively. This can lead to software that falls short in terms of accessibility.
Another common barrier is the misconception that accessibility is a one-size-fits-all approach. In reality, accessibility needs can vary greatly depending on the individual and their specific disabilities. Designers and developers need to consider a range of accessibility options and provide customizable features that allow users to adapt the software to their specific needs.
Providing options for font size adjustment, color contrast settings, and keyboard shortcuts can significantly improve accessibility for users with visual impairments or motor disabilities. By offering these customizable features, businesses can ensure their software caters to a wide range of users.
The impact of accessibility on user experience
For individuals with disabilities, accessible software can be life-changing. It allows them to independently access information, communicate with others, and perform tasks that were previously inaccessible. This empowerment can have a profound impact on their quality of life and overall well-being.
In addition to benefiting individuals with disabilities, accessible software also improves the user experience for all users. For example, captioning videos not only benefits individuals with hearing impairments, but it also allows users to watch videos in environments where sound may not be practical, such as in a quiet office or a noisy public space.
Accessible software also tends to have cleaner and more organized interfaces, making it easier for all users to navigate and find the information they need. By prioritizing accessibility, businesses can create software that is intuitive and user-friendly for everyone.
Business benefits of investing in accessible software
Investing in accessible software has numerous benefits for businesses. In addition to enhancing loyalty among employees and customers, accessible software can open up new market opportunities. The Bureau of Internet Accessibility reports Forrester Research estimated accessibility and improvements yield $100 for every $1 spent. Also, in a post about driving growth via accessibility, Forrester noted the disability community has an annual disposable income of $1.9 trillion. By catering to individuals with disabilities, businesses can tap into a customer base that may have been underserved in the past.
From a legal standpoint, accessibility is also a requirement in many jurisdictions. Failure to comply with accessibility standards can result in legal consequences and damage to a company’s reputation.
Tools and technologies for testing accessibility
Ensuring accessibility in custom software development requires the use of specialized tools and technologies for testing. These tools help designers and developers identify and fix accessibility issues, ensuring the software meets the needs of users with disabilities. Some commonly used tools in the industry include:
Screen readers: These audio readers are essential tools for individuals with visual impairments. They read aloud the content displayed on the screen, allowing users to navigate and interact with the software. Developers can use screen readers to test the accessibility of their software and make necessary adjustments to improve the user experience.
Color contrast analyzers: Color contrast is crucial for individuals with visual impairments or color blindness. Using color contrast analyzers, developers can ensure the color combinations used in their software meet the minimum contrast requirements for readability. This tool helps in creating a visually inclusive design that is accessible to all users.
Keyboard navigation testers: Keyboard navigation is vital for individuals who cannot use a mouse or have motor disabilities. Testing the software’s functionality using only a keyboard is essential to ensure all features and functionalities are accessible via keyboard navigation. Theses testers simulate keyboard inputs and allow developers to identify and fix any issues related to navigation.
Automated accessibility testing tools: There are various automated accessibility testing tools available that can scan the software’s code and identify potential accessibility issues. These tools analyze HTML, CSS and JavaScript code to check for compliance with accessibility standards and guidelines. They provide detailed reports and suggestions for improvement, making it easier for developers to address accessibility concerns.
It’s important to note these tools are typically used in conjunction with manual testing and user feedback to achieve the best results.
Embracing accessibility for a more inclusive digital future
Embracing accessibility in custom software development is not just about complying with legal requirements; it is about creating a more inclusive digital future. By unlocking the possibilities of accessibility, businesses can tap into new markets, improve user experience for all users, and demonstrate their commitment to creating technology that is accessible to everyone.
When you’re ready to engage a software development firm, include accessibility requirements in procurement processes. This ensures the services provided meet accessibility standards and align with your accessibility goals.
Growth Acceleration Partners can guide companies through the complexities of accessibility. Start your journey toward software accessibility for all — let’s connect.



